Complication rates low in study population
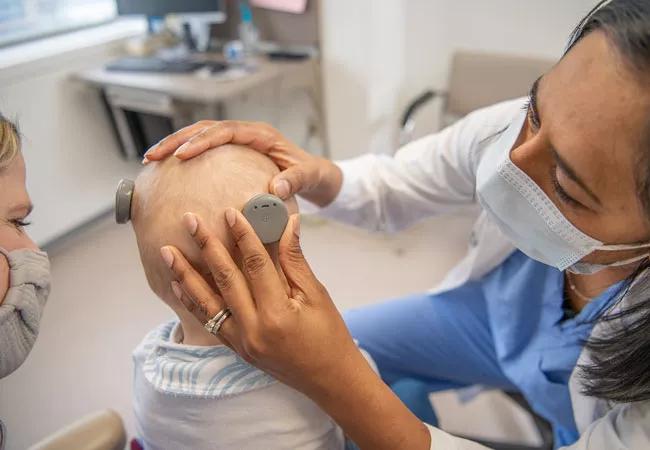
Auditory input is essential to the development of critical speech, language and communication skills in children. Lacking this auditory input, children with hearing loss are at risk for deficits in cognitive development, psychosocial hardship and educational difficulties. For these children, cochlear implantation can make a dramatic difference. Studies have found similar rates of speech and language development in children younger than one year who had cochlear implantation compared to age-matched normal-hearing children and improved outcomes compared to children who had the procedure at an older age.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Since cochlear implantation was first approved for children 24 months and older in 1998, the approval age has steadily decreased, most recently to nine months. Despite the proven benefits of cochlear implantation in this young population, there are many unique physiologic and anatomic considerations that require surgical and anesthesia expertise to avoid complications.
The Cleveland Clinic pediatric cochlear implant program performs cochlear implantation in patients as young as seven months. Clinic investigators participated in a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature on complications associated with cochlear implantation in children 12 months and younger.
The study appeared in Journal of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery.
The investigators found 18 studies that met the study criteria; they included 449 patients from four to 12 months who underwent 625 cochlear implants. Across the studies, there were 27 major complications and 35 minor complications. Major complications occurred in 2.3% of cochlear implantations and 3.1% of patients; they included 10 device failures, eight CSF leaks, three device migrations, three infections and one of each of the following: blood transfusion, temporary facial paralysis and skin breakdown requiring revision.
Minor complications occurred in 1.8% of cochlear implantations; they included four seromas/hematomas, four minor wound issues, two temporary balance disturbances, two channel anomalies, and one of each of the following: pressure ulcer, infection, wound dehiscence and intraoperative sacrifice of chorda.
Advertisement
These findings are comparable to large-scale studies of cochlear implantation in adults and children over 12 months, which have reported major complication rates ranging from 0.7% to 8.9% and minor complication rates ranging from 2% to 16.1%.
“The literature supports the safety of early implantation. Early acquisition of sound is so important for children with hearing loss. The earlier they can safely have cochlear implants, the better the outcomes,” says Samantha Anne, MD, study investigator and an otolaryngologist at Cleveland Clinic.
No complications related to anesthesia were reported. “It’s also important to be cautious about the duration of surgery. It requires an experienced and skilled surgeon to safely perform the procedure in younger patients without an extended duration of surgical and anesthesia time,” says Dr. Anne.
At Cleveland Clinic, when a child doesn’t pass a hearing screen, they receive a comprehensive medical and audiological evaluation. This includes testing to identify the cause of their hearing loss, fitting hearing aids, and monitoring speech and language development. When a child doesn’t have adequate improvement with hearing aids and there is poor progression of speech and language milestones, the entire team discusses cochlear implantation with the parents. “With this study, we can inform parents that the literature supports implantation at less than 12 months,” says Dr. Anne.
A recent case typifies the positive outcomes in younger patients: a seven-month-old who had cochlear implantation made rapid progress, babbling and responding to sound within two months, developing at the same pace as his hearing peers. Cleveland Clinic is currently completing a systematic review of auditory outcomes with cochlear implantation in this age group.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Analysis of HNSCC patients shows HPV status to be predictive of higher abundance of oncobacteria within the tumor

Case study illustrates the potential of a dual-subspecialist approach

Evidence-based recommendations for balancing cancer control with quality of life

Study shows no negative impact for individuals with better contralateral ear performance

HNS device offers new solution for those struggling with CPAP

Patient with cerebral palsy undergoes life-saving tumor resection

Specialists are increasingly relying on otolaryngologists for evaluation and treatment of the complex condition

Detailed surgical process uncovers extensive middle ear damage causing severe pain and pressure.