Patients can expect to stay active, enjoy high sports function and quality of life

A new study shows quality of life and sports-related function was sustained for many patients 10 years out from anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) repair.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The award-winning study was presented by Kurt P. Spindler, MD, orthopaedic surgeon and Vice Chairman of Research, Cleveland Clinic Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute, at the 2017 American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine’s annual meeting in Toronto. It was recently published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine.
In addition, the Multicenter Orthopaedics Outcome Network (MOON) group and Dr. Spindler were recognized with the society’s annual O’Donoghue Sports Injury Research Award for the best overall clinical research paper.
Dr. Spindler and fellow MOON researchers demonstrated that patients could perform sports-related functions and maintain a high knee-related quality of life a decade after surgery, though activity levels did decline over time.
“Our data show significant improvements in patient-reported outcome measures (sports function and quality of life) two years after surgery, which was maintained at six and 10 years,” says Dr. Spindler. “These improvements were noted across a substantial population of 1,320 patients, who made up 83 percent of our original study group.”
A total of 1,597 patients with unilateral ACL reconstructions were identified and enrolled in the trial between 2002 and 2004 from seven sites in the MOON group, including Cleveland Clinic. Of those treated, 90 percent underwent a primary ACL reconstruction, and 10 percent a revision ACL reconstruction procedure. Graft choice was 42 percent autograft bone-patellar-bone, 31 percent autograft soft tissue and 27 percent allograft.
Advertisement
Patients completed a preoperative series of validated outcome instruments, including the International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC), Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) and Marx activity scale (Figure 1).
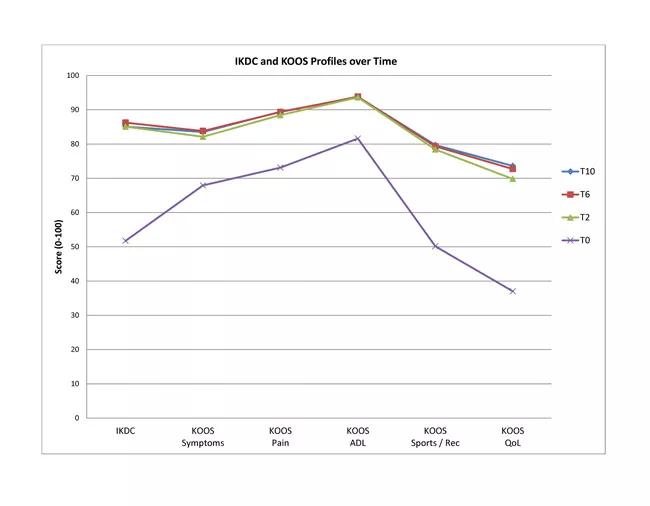
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/de6e5c5c-158c-4a1a-a9b8-34baeef372c8/17-ORT-1253-Spindler-Inset-Image-01-650pxl-width_jpg)
Both IKDC and KOOS scores significantly improved after two years and were maintained at six and 10 years.
Two-year follow-up was obtained for 1,379 patients (57 percent male; median age 23 years), six-year follow-up for 1,375, and 10-year follow-up for 1,320 patients. The latter represents 83 percent of the original study group, making this the first prospective ACL reconstruction cohort with over 80 percent follow-up at 10 years.
Subsequent surgery data was obtained on over 90 percent of the cohort.
Interestingly, Dr. Spindler says, Marx activity level scores dropped markedly over time. Significant drivers of poorer outcomes included lower baseline scores prior to surgery, higher body mass index, smoking, a history of medial meniscus surgery prior to ACL reconstruction, having a revision ACL reconstruction, grades 3-4 articular cartilage pathology, and having any subsequent ipsilateral surgery. Graft type, MCL or LCL pathology, and medial and lateral meniscus surgery at the time of ACL reconstruction were not found to be significant risk factors (Table 1).
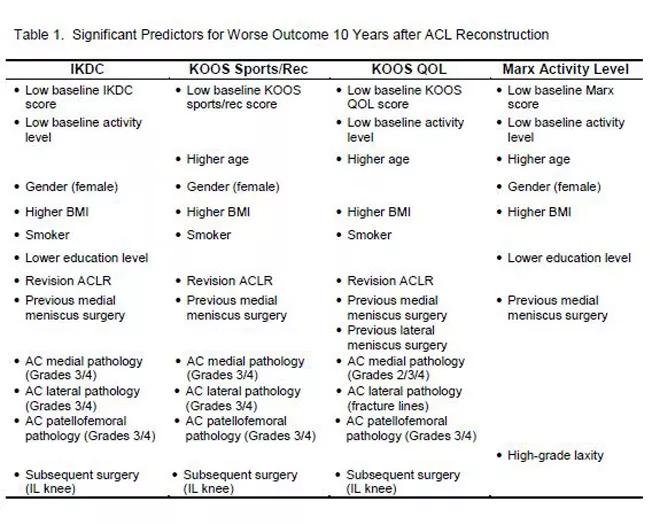
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/44011c57-e6d1-40c6-af7d-880c37dbeaff/17-ORT-1253-Spindler-Inset-Image-02_jpg)
“An active patient may view an ACL injury as devastating, but our research adds to short- and long-term studies that show a good prognosis for sports function and quality of life,” Dr. Spindler reports.
“This study can help medical providers continue to make good treatment decisions, and present these injuries as simply a setback,” Dr. Spindler notes. “The prognostic information will aid in setting the patient’s expectations after ACL reconstruction and in counseling to emphasize that managing modifiable risk factors will significantly influence their outcome.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

How it’s similar but different from the direct anterior approach

Collaboration must cross borders and disciplines

Systematic review of MOON cohorts demonstrates a need for sex-specific rehab protocols

Should surgeons forgo posterior and lateral approaches?

How chiropractors can reduce unnecessary imaging, lower costs and ease the burden on primary care clinicians

Why shifting away from delayed repairs in high-risk athletes could prevent long-term instability and improve outcomes

Multidisciplinary care can make arthroplasty a safe option even for patients with low ejection fraction

Percutaneous stabilization can increase mobility without disrupting cancer treatment