Magnet-driven growth rods are effective, less invasive for select patients
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Skeletal traction is a useful and time-tested preoperative treatment for children and adolescents with severe scoliosis. Studies have demonstrated that it can improve curve flexibility and subsequently help achieve optimal curve correction during spinal fusion. However, traction set-ups are bulky, uncomfortable and significantly restrict mobility. As a consequence they are extremely unpopular with patients and their families.
In the following case study, an external, magnetically-driven distraction rod system that came onto the market five years ago provided an alternative way to enhance curve flexibility without the use of skeletal traction in an adolescent scoliosis patient.
The NuVasive MAGEC® system (Magnetic Expansion Control System), comprising magnetic spinal rods and a hand-held external remote controller, was cleared by the FDA in 2014 for treatment of young patients with severe progressive spinal deformities who are at risk of developing thoracic insufficiency syndrome. Its common use is as a less-invasive alternative to traditional growing rods, which can minimize the progression of scoliosis in young patients for whom bracing is not appropriate or unlikely to be tolerated. However, instead of requiring repeated surgeries every six months for manual distraction, the magnetic rods can be lengthened, using an external magnet system, during a short in-office procedure every three months. Lengthening can be tailored to the patient and are typically 3 mm to 6 mmm at a time.
Advertisement
A Cleveland Clinic patient with severe adolescent idiopathic scoliosis was among the first U.S. patients for whom the device was used for internal traction as part of a staged procedure.
A 14-year-old girl presented at Cleveland Clinic with advanced, severe adolescent idiopathic scoliosis of the thoracolumbar region. Radiographs revealed a thoracic and lumbar curve in excess of 90 degrees with an axial rotation in excess of 70 degrees. An Adams forward bend test showed a dramatic and severe R rib prominence and markedly abnormal waist and shoulder asymmetry.
The patient rated her back discomfort at seven on a scale from one to 10, with increasing pain when sitting for more than 30 minutes and during activity.
After discussing in detail the options for treatment with the patient and her family, they agreed to magnetic rod placement and weekly distraction for eight to 12 weeks, followed by a formal spinal fusion.
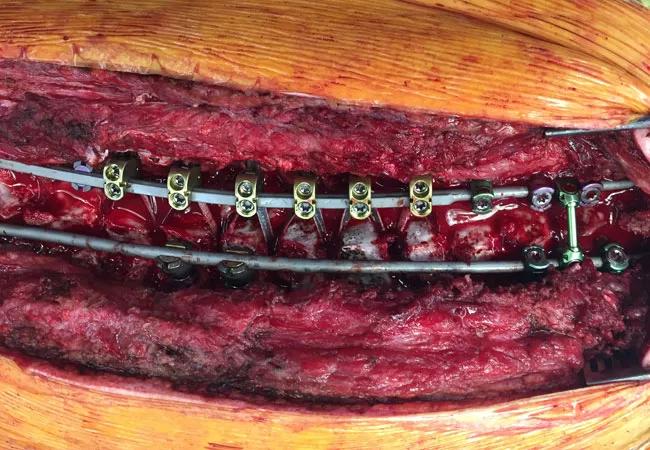
During the initial surgery, a magnetic rod was placed on either side of the spine, with screws placed bilaterally in L3 and L4 and hooks placed at T3, T4 and T5 on the left side and T9 and T10 on the right. The curve was markedly stiff, and paraspinal musculature was tight.
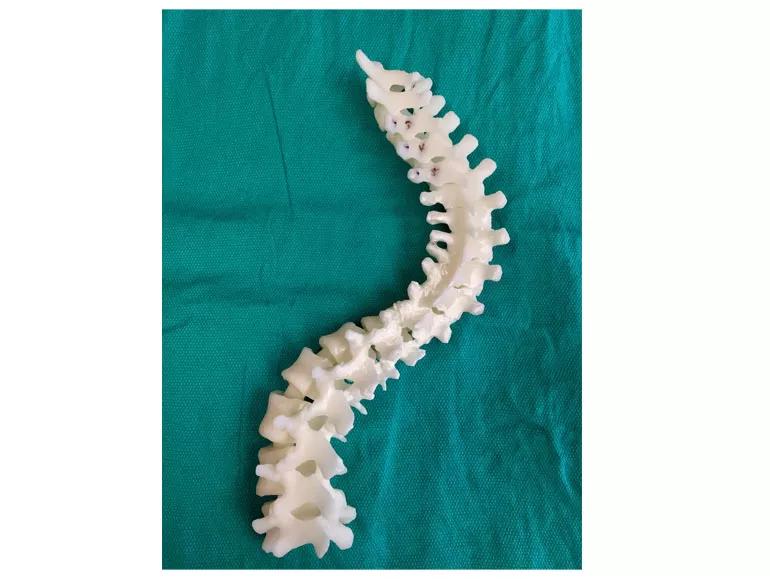
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/cfbb431f-1981-4c26-8c19-a7ea5a1c8b99/19-ORT-1029-scoliosisSpine-spineOnGrn-Inset_770x579_jpg)
To facilitate operative planning and intraoperative decision making, a life-size model of the thoracic and lumbar spine was printed, then sterilized, to be available to examine during the procedure.
An innovative new aspect of the procedure was the addition of a life-size 3D printed model of the spinal column based on a high resolution CT scan of the patient. In preoperative planning, this model was useful in helping the surgical team get a sense of the anatomy of the complex rotational deformity as well as pedicle size and orientation. The 3D model was useful during the procedure to help ensure that screws were placed accurately.
Advertisement
After surgery, weekly distractions of the rods were performed on the patient in the office setting. The titanium rods have an internal magnet that is activated by an external device placed against the child’s bare back. Powerful magnets within the device cause the magnet in the rod to rotate, and thus the rod is slowly and accurately lengthened.
Over the course of three months, the patient achieved marked improvement in curvature and flexibility and did not make any complaints of pain from the distraction procedure.
Three months after implantation, the magnetic growing rods were surgically removed, and new permanent, segmental spinal instrumentation was placed along with graft material to achieve spinal fusion.
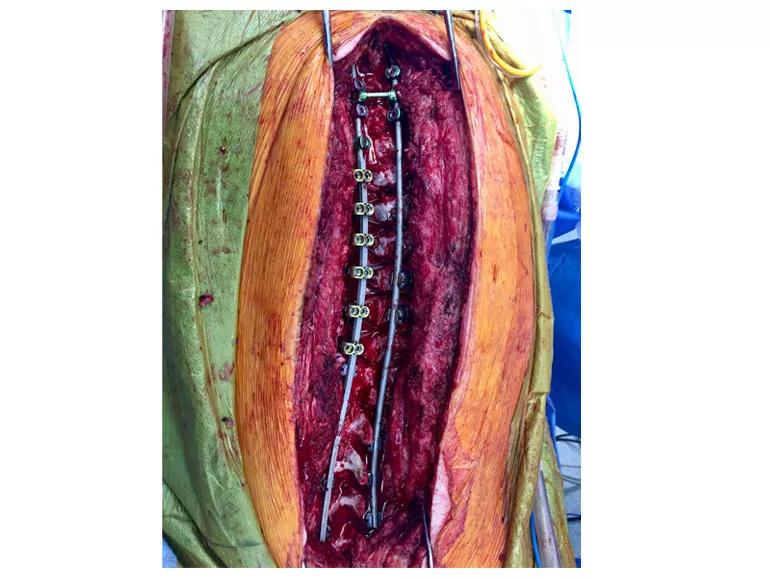
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/83462310-f9f5-4c52-a205-ddbd532ee566/19-ORT-1029-scoliosisSpine-surg-Inset_770x579_jpg)
Intraoperative photograph of the final construct; note the hybrid fixation of hooks, sublaminar nylon bands and pedicle screws.
Now, at nine months post-op, the patient is doing well. She is back in school full-time and living pain-free, with a whole new outlook on life owing to a dramatically improved alignment.
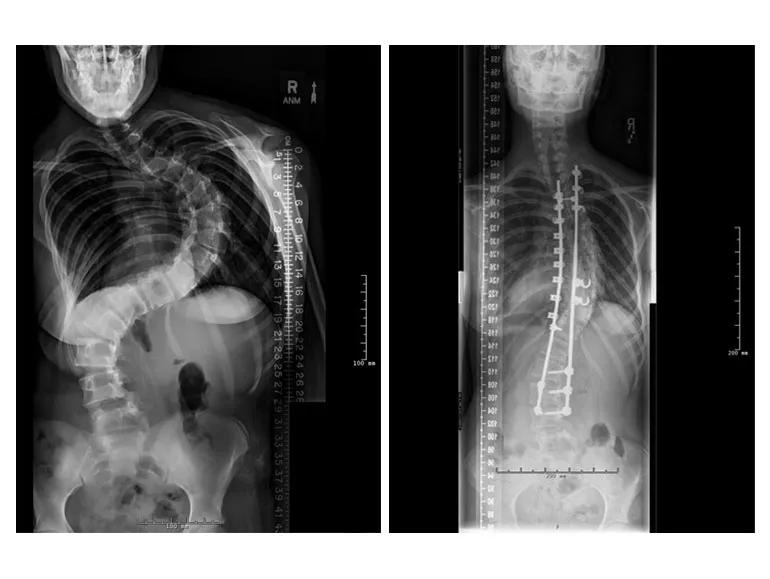
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/d607ea55-69ba-43fa-9a65-0c28dd38e8b6/19-ORT-1029-scoliosisSpine-Xrays2-Inset_770x579_jpg)
X-rays show the curvature of the patient’s spine before implantation of the magnetic rods, and seven months after spinal fusion and placement of permanent rods.
This device appears to be a promising, less invasive alternative to preoperative skeletal traction, with reduced pain and immobility for the patient. European studies demonstrate and endorse the use of magnetic rods for this application, which have given us another tool for the management of advanced spinal deformity.
Advertisement
Advertisement

How it’s similar but different from the direct anterior approach

Collaboration must cross borders and disciplines

Systematic review of MOON cohorts demonstrates a need for sex-specific rehab protocols

Should surgeons forgo posterior and lateral approaches?

How chiropractors can reduce unnecessary imaging, lower costs and ease the burden on primary care clinicians

Why shifting away from delayed repairs in high-risk athletes could prevent long-term instability and improve outcomes

Multidisciplinary care can make arthroplasty a safe option even for patients with low ejection fraction

Percutaneous stabilization can increase mobility without disrupting cancer treatment