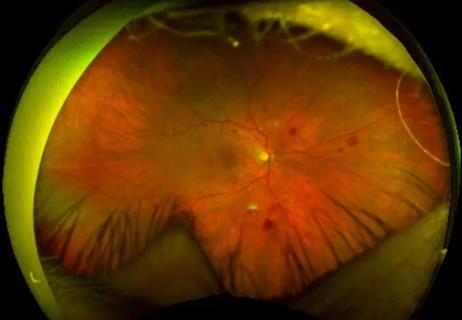
Study identifies factors that may predict vision outcomes in diabetic macular edema

Study highlights the value of quantitative ultra-widefield angiography
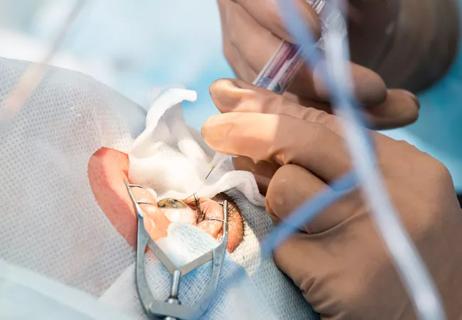
How to screen for and manage treatment-triggered uveitis
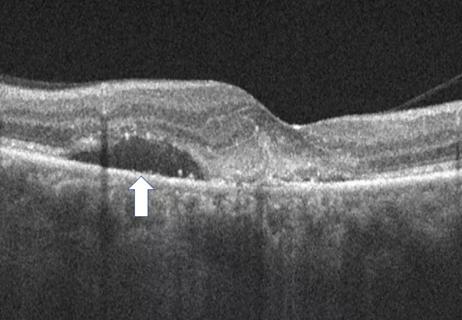
Advanced OCT features may help individualize treatment intervals
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
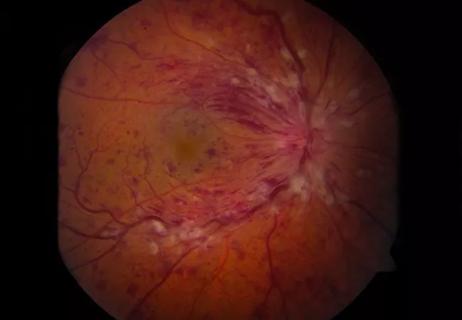
Intraretinal fluid volumes and other features detectable with OCT may help predict treatment response

53% of participants didn’t need anti-VEGF for six months or longer

Faricimab every 16 weeks offers similar benefits as aflibercept every eight weeks
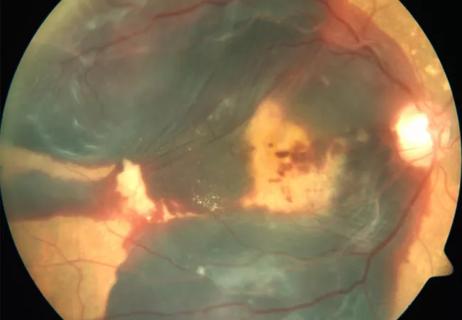
Patients with diabetic eye disease are most affected

Severity of diabetic retinopathy is a useful predictor
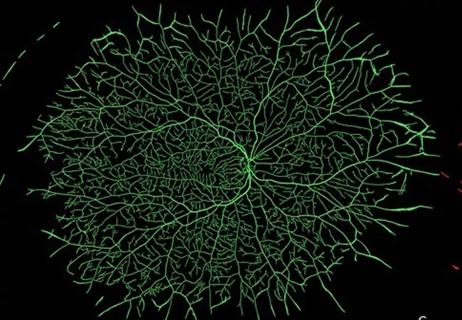
Radiomics analysis suggests underlying subvisual features may encode information related to tolerance of interval extension in retinal vascular disease
Advertisement
Advertisement