
Unraveling the TNFA receptor 2/dendritic cell axis

Older Psoriasis Patients May Experience Quicker Transition
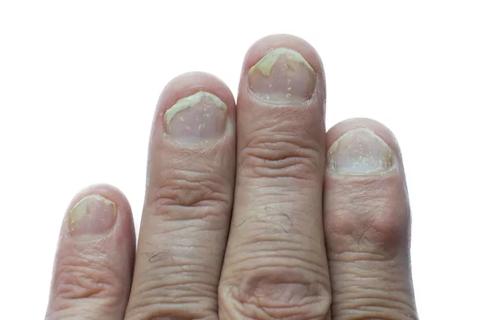
Genetic polymorphisms and response to TNFα blockers

The potential for safer therapies
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
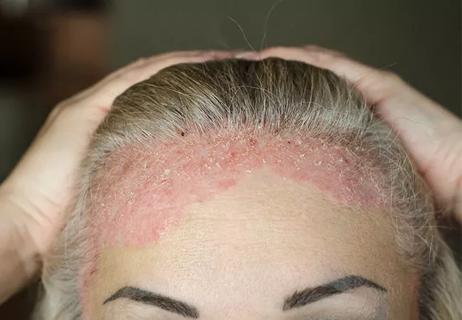
Patient reported outcomes differentiate between remission and low disease activity in PsA
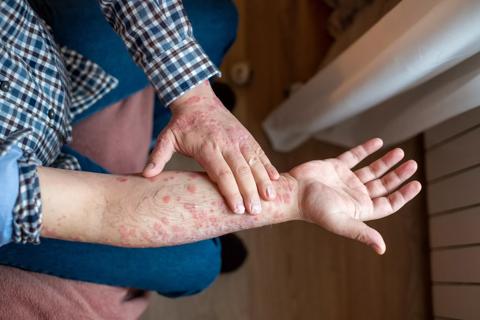
Co-management increases opportunities for research and education

Defect in myosin binding may explain why a significant percentage of patients do not adequately respond to anti-TNF therapy
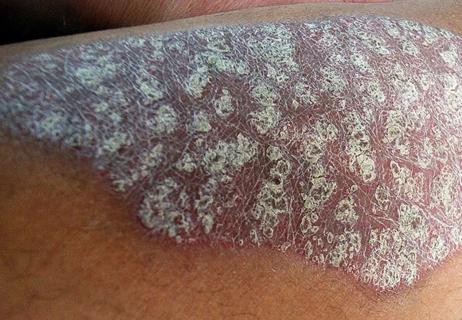
Study finds significant histologic differences between TNFi-induced psoriasis and idiopathic psoriasis
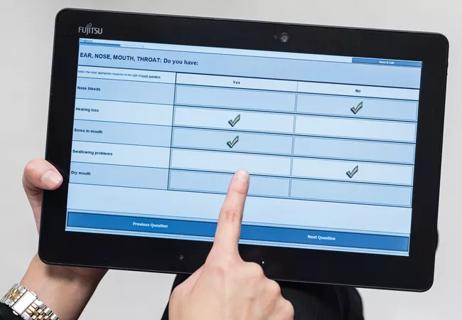
Patients with minimal disease activity report better physical and mental health as well as less fatigue
Husni lab recently funded by NIH-NIAMS
Advertisement
Advertisement